Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition affecting millions globally. While not life-threatening, it can significantly impact physical comfort, emotional well-being, and social interactions. This comprehensive guide explores the various types of psoriasis, its causes, triggers, and effective management strategies to help you lead a fulfilling life.
Understanding the Different Types of Psoriasis
Psoriasis manifests in several forms, each with unique characteristics:
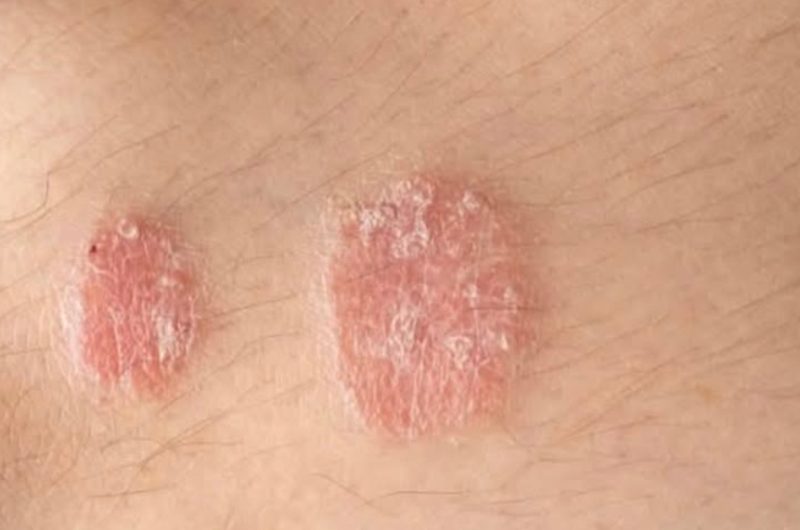
- Plaque Psoriasis: The most common type, featuring raised, red patches covered with silvery scales.
- Guttate Psoriasis: Small, drop-like spots often appearing after a strep throat infection.
- Pustular Psoriasis: Red skin with pus-filled blisters, less common but distinct.
- Inverse Psoriasis: Affects skin folds like armpits, groin, and under breasts.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis: Severe form with widespread redness and peeling, requiring immediate medical attention.
Psoriasis is not contagious and cannot be spread through physical contact.
Causes and Triggers of Psoriasis
The exact cause remains unknown but involves genetic and environmental factors:
- Genetic Predisposition: Family history increases risk.
- Immune System Dysfunction: The immune system attacks healthy skin cells, causing rapid growth and symptoms.
Common triggers include:
- Infections: Strep throat can trigger guttate psoriasis.
- Stress: Emotional and physical stress exacerbates symptoms.
- Skin Injuries: Cuts, scrapes, or sunburn can trigger flare-ups (Koebner phenomenon).
- Medications: Beta-blockers and lithium may worsen symptoms.
- Alcohol and Smoking: Excessive alcohol and smoking increase severity and risk.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosis involves a physical exam by a dermatologist, sometimes requiring a skin biopsy. Treatment focuses on symptom management and includes:
- Topical Medications: Corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, and salicylic acid reduce inflammation and scales.
- Light Therapy: UV light slows skin cell growth and reduces inflammation.
- Systemic Medications: Oral or injectable medications for moderate to severe cases.
Living with Psoriasis
Managing psoriasis requires a proactive approach:
- Identify and avoid personal triggers.
- Practice stress management techniques.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle with balanced diet and exercise.
- Connect with support groups or online communities for emotional support.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only. Consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.